Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
This study presents the results of multiphysics analysis, which investigates the change of reactivity caused by the motion of fluids, of Windscale Works criticality accident. The purpose of this study is to confirm previously reported trends of emulsion formation and increase in reactivity by the multi-physics analysis which takes the motion of fluids into account. Continuous energy Monte Carlo code MVP3 was used to calculate reactivity based on the material distribution obtained by CFD calculation using OpenFOAM. An interface program in python was developed to transfer data from OpenFOAM to MVP3. The change of reactivity caused by the motion of solutions was calculated without considering the generation of heat by fissions in a system that simulated the transfer vessel at Windscale Works. As a result, trends of emulsion formation and increase in reactivity were confirmed. The influence of the resolution of the calculation system on the results was also discussed.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
A Monte Carlo Solver Solomon has been under development as an object-oriented code written in the C++14 standards. It consists of regular capabilities of criticality safety analysis and a special capability of random media criticality. In the latter capability, Solomon is equipped with a class for the random media modeled by the incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). By this modeling, the uncertainty of random media criticality can be evaluated by executing criticality calculations over many IRWF-replicas. However, it is impossible to know beforehand how many IRWF-replicas should be computed. To deal with this issue, a bounded amplification (BA) technique has been newly equipped in Solomon. Applying BA to IRWF, it is possible to reduce the number of IRWF-replicas by more than 95% in terms of the upper limit estimation of neutron effective multiplication factor. Solomon is also equipped with a voxel-overlay (VO). This functionality is shown to be valuable for evaluating the resonance self-shielding effect.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The criticality accident that resulted in the evacuation of residents occurred on September 30, 1999, at JCO's nuclear fuel fabrication plant in Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. This paper presents the outline, technical issues and background of the accident and the situations that followed. The review of this accident was one of the hot issues in the last ICNC2003 organized in Tokai-mura. At the this turn of ICNC in Japan, we would like to revisit the accident to reaffirm and share the idea that the response and preparedness should be strengthened to protect people and the environment from nuclear disasters. The accident occurred in a factory of JCO during the informal and unusual process of preparing a uranium nitrate solution of medium-enriched (18.8 weight%  U) uranium from U
U) uranium from U O
O using the precipitation tank of 45 cm in diameter, which exceeded the critical diameter (ca. 23 cm) of an infinite cylinder with a full thick water reflector. A 2.2-cm-thick water "jacket" surrounded and enclosed the tank, and the jacket was connected to the cooling tower beside the factory. The jacket not only functioned as the neutron reflector but also prevented the evaporation of the solution, and then the criticality continued for about 20 hours. Because JCO's plant had not anticipated the criticality accident, the response to the accident was confusing. During the accident, the JAERI and JNC, both the predecessors of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), acted to terminate the criticality and reduce the residents' exposure to radiation. After the accident, the JAERI and the National Institute of Radiological Sciences provided the telephone consultation at the village office of Tokai-mura. The JNC did the same things at the prefectural building of Ibaraki to advise the residents. The presentation may include issues of applying the Slide rule, identifying a nuclear criticality accident to occur, and responding to the emergency.
using the precipitation tank of 45 cm in diameter, which exceeded the critical diameter (ca. 23 cm) of an infinite cylinder with a full thick water reflector. A 2.2-cm-thick water "jacket" surrounded and enclosed the tank, and the jacket was connected to the cooling tower beside the factory. The jacket not only functioned as the neutron reflector but also prevented the evaporation of the solution, and then the criticality continued for about 20 hours. Because JCO's plant had not anticipated the criticality accident, the response to the accident was confusing. During the accident, the JAERI and JNC, both the predecessors of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), acted to terminate the criticality and reduce the residents' exposure to radiation. After the accident, the JAERI and the National Institute of Radiological Sciences provided the telephone consultation at the village office of Tokai-mura. The JNC did the same things at the prefectural building of Ibaraki to advise the residents. The presentation may include issues of applying the Slide rule, identifying a nuclear criticality accident to occur, and responding to the emergency.
Gunji, Satoshi; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY". The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the core configurations of the new STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two sets of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called STACY from a solution system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system to validate computation results of criticality characteristics of fuel debris generated in the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To experimentally simulate the composition and characteristics of fuel debris, we will prepare several grid plates which make particular neutron moderation conditions and a number of rod-shaped concrete and stainless-steel materials. Experiments to evaluate fuel debris's criticality characteristics are scheduled using these devices and materials. This series of STACY experiments are planned to measure the reactivity of fuel debris-simulated samples, measure the critical mass of core configurations containing structural materials such as concrete and stainless steels, and the change in critical mass when their arrangement becomes non-uniform. Furthermore, two divided cores experiments are scheduled that statically simulate fuel debris falling, and also scheduled that subcriticality measurement experiments with partially different neutron moderation conditions. The experimental plans have been considered taking into account some experimental constraints. This paper shows the schedule of these experiments, as well as the computation results of the optimized core configurations and expected results for each experiment.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s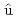 ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Murakami, Takahiko; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
New experiments simulating fuel debris in the new criticality assembly, STACY, are designed to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations for criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. In the new STACY experiment, a two-region core consisting of a driver region and a test region was investigated in order to configure a debris-simulated core with under-moderation condition (lattice pitch 1.27-cm) having the constraint of available fuel rod number. The test region with a 1.27-cm lattice pitch is surrounded by the driver region, in which fuel rods are arranged in a checkerboard pattern on a 1.27-cm lattice plate, with a 1.80-cm lattice pitch. Neutron spectra and sensitivity were calculated by using MCNP6 and ENDF/B-VII. The core which has a 17 17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17
17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17 17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13
17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13 13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of
13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of  Si and
Si and  Ca (n,
Ca (n, ) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Murakami, Takahiko; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Hasegawa, Kenta; Tada, Yuta; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 4th Reactor Physics Asia Conference (RPHA2023) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/10
To conduct integrated thermal power measurements for the performance test of the modified STACY, we re-analyzed the experimental data measured in the solution fuel STACY using the activation method. We validated its feasibility under the limited number of activation detectors. The re-analyzed results of the activation method by using MVP and PHITS with JENDL-4.0 indicated that the effect of the difference of the position between activation detectors was small enough, and the results agreed with that of the fission product analysis within almost 10%. It is conceivable that the activation method could be adopted instead of the fission product analysis.
 variations by nonuniform core configurations
variations by nonuniform core configurationsGunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Suyama, Kenya
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 197(8), p.2017 - 2029, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fuel debris generated by the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is expected to have not only heterogeneous but also nonuniform compositions. Similarly, damaged fuel assemblies remaining in the reactor vessels also have nonuniform configurations due to some missing fuel rods. This non-uniformity may cause changing neutron multiplication factors. The effect of non-uniformity on the neutron multiplication factor is clarified by computations, and the possibility of experimentally validating the computations used for criticality management is being investigated. For this purpose, in this study the criticality effects of several core configurations of a new critical assembly, STACY, of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency with nonuniform arrangements of uranium oxide fuel rods, concrete rods, and stainless-steel rods were studied to confirm benchmarking potential. The difference in these arrangements changed the neutron multiplication factor by more than 1 $. We confirmed that changes in local neutron moderation conditions and the clustering of specific components caused this effect. In addition, the feasibility of benchmark experimental cores with nonuniform arrangements is evaluated. If benchmarking of such experiments could be realized, it would help to validate calculation codes and to develop criticality management methods by machine learning.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 20th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM22) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/06
Since the 1990s, the importance of the handbook has changed significantly, as the computational power has improved and continuous energy Monte Carlo codes have become widely used, which enables highly accurate criticality calculations, when necessary, irrespective of the complexity of the system. Because the value of performing a large number of calculations in advance and summarizing the data has decreased, since the second edition was published publicly in 1999, there has been no revision of criticality safety handbooks in Japan for nearly a quarter of a century. In Japan, where the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident occurred in 2011, it became necessary to deal with criticality safety issues in the transport and storage of the fuel debris which contains complex constituent elements, and the summary the criticality safety management for such material is an urgent issue. In the area of burnup credit, the transport and storage of fuel assemblies with low achieved burnups due to the consequences of accidents might be the problem. In addition, nuclear data, which is the input for the continuous energy Monte Carlo code, has been improved several times, now JENDL-5 is available from the end of 2021, and its incorporation becomes a need in the field. This report provides an overview of the latest criticality safety research in Japan and the planned revision of the Criticality Safety Handbook, which could be applied to the transport and storage sectors.
Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has tackled the experimental approach for determining the criticality of pseudo-fuel debris plausibly simulating actual fuel debris since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. To elucidate the characteristics of the pseudo-fuel debris, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency modified the STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) to conduct critical experiments simulating fuel debris. Thus, we proposed three types of modified STACY core configurations. In critical experiments in the modified STACY core, it is important to judge whether the proposed modified STACY core configurations are representative of molten core-concrete interaction debris or not. In this study, we built pseudo-fuel debris models considering a volume ratio of pseudo-fuel debris to moderation (V /V
/V ) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C
) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C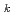 ) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V
) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V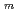 /V
/V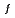 values. The main contributions to C
values. The main contributions to C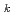 values were
values were  U
U  ,
,  U
U  , and
, and  Fe (n,
Fe (n, ), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 159, p.104630_1 - 104630_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this work, the methodology of Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) is applied to criticality tallies in Monte Carlo fission source cycles in order to evaluate the utility value of the distribution tail ends. Numerical results obtained under a sufficiently large number of particles per cycle show that the extreme value index (EVI) in GEV falls within the range of Weibull distribution including the EVI of Gumbel distribution as the role of a boundary value layer. GEV is also applied to a historically-challenging loosely-coupled system for demonstrating population diagnosis under an insufficient number of particles per cycle. It turns out that the transition from one equilibrium to other equilibrium makes the EVIs of upper and lower distribution tail ends depart from each other so that one of them falls in the range of Weibull distribution and the other in that of Frechet distribution.
Higemoto, Wataru; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Ito, Takashi; Suzuki, Taiga*; Raymond, S.*; Yanase, Yoichi*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(49), p.e2209549119_1 - e2209549119_6, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yui*; Yamamoto, Arisa*; Sato, Naoki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ohara, Koji*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Mori, Takao*; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134111_1 - 134111_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yokoyama, Kenji; Taninaka, Hiroshi
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (132), p.25 - 33, 2022/06
This article explains the results of integral test of JENDL-5 by benchmark analysis in fast reactor system, which were presented in a special session of the 2022 Spring Annual Meeting of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ). The latest version of Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5, was released in December 2021. In order to confirm the applicability of JENDL-5 to the fast reactor system, we conducted a set of benchmark analysis using the integral experiment data included in the fast reactor nuclear design database which is being developed by JAEA. With respect to major nuclear characteristics in the standard fast reactor system, it was confirmed that the ratios of analysis result and experimental result (C/E values) based on JENDL-5 were almost the same as those of JENDL-4.0. In the special session, the results of sensitivity analysis were reported. Since the results have been described in the proceedings of the AESJ meeting, we add the results of the versions under development of JENDL-5 and discuss their relationship with the reported results of sensitivity analysis.
 )O
)O (
( = Th, Np) prepared by supercritical hydrothermal synthesis
= Th, Np) prepared by supercritical hydrothermal synthesisShirasaki, Kenji*; Tabata, Chihiro*; Sunaga, Ayaki*; Sakai, Hironori; Li, D.*; Konaka, Mariko*; Yamamura, Tomoo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 563, p.153608_1 - 153608_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We focused on the direct synthesis of (U,  )O
)O solid solution (
solid solution ( =Th, Np) by extending our recent progress in hydrothermal synthesis with additives. The homogeneity of the (U,
=Th, Np) by extending our recent progress in hydrothermal synthesis with additives. The homogeneity of the (U,  )O
)O (
( = Th, Np) systems prepared by supercritical hydrothermal reactions was investigated through crystallographic analysis based on Vegard's law, and the
= Th, Np) systems prepared by supercritical hydrothermal reactions was investigated through crystallographic analysis based on Vegard's law, and the  Na nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement of (U, Np, Na)O
Na nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement of (U, Np, Na)O solid solutions. Our experimental and analytical results revealed that (i) an optimal additive is ammonium carbonate and starting uranium valence is IV in the case of (U, Th)O
solid solutions. Our experimental and analytical results revealed that (i) an optimal additive is ammonium carbonate and starting uranium valence is IV in the case of (U, Th)O , and (ii) an optimal additive is ethanol and starting uranium valence is VI in the case of (U, Np)O
, and (ii) an optimal additive is ethanol and starting uranium valence is VI in the case of (U, Np)O , for producing the homogeneous solid solutions by hydrothermal synthesis.
, for producing the homogeneous solid solutions by hydrothermal synthesis.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Suyama, Kenya; Izawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/05
The fuel debris is expected to have not only heterogeneous but also non-uniform compositions. Therefore, the calculation method used in their criticality management is required to be validated experimentally. In this study, several core configurations of a new critical assembly "STACY" of JAEA with non-uniform arrangements of uranium oxide fuel rods, concrete rods and stainless steel rods, which are components of the fuel debris, were studied. In each case, the median value of 100 sample patterns was larger than the mean effective multiplication factor. It was also confirmed that there are differences in the effective multiplication factor of more than one dollar by the pattern changing, and that the neutron spectra can change significantly by changing the local neutron moderation conditions. In particular, the effective multiplication factor became smaller when over-moderated regions with large water-to-fuel ratios were formed in the core configurations due to increases in thermal neutron absorption. Such criticality experiments with non-uniform arrangements of multiple compositions will be useful to evaluate the validity of the calculation code.
Katano, Ryota; Nishihara, Kenji; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Meigo, Shinichiro
JAEA-Research 2021-016, 16 Pages, 2022/03
It has to be confirmed that the accelerator-driven system (ADS), which is dedicated to transmuting minor actinides, is subcritical in any state by measurements. In the previous research, we have proposed a procedure in which the core safely and efficiently approaches the target subcriticality before the operation. In this procedure, the reference value of the subcriticality at the initial state is measured by the area ratio method capable of the absolute value measurement. The area ratio method uses a pulsed neutron source. However, specific and practical parameters of the accelerator for the area ratio method have not been determined. In this study, we determined the accelerator parameters with the consideration of the uncertainties derived by the dead-time of the detector and the statistical error of the count ratio. In addition, we estimate the coating amount of the sample nuclide in the assumption of the use of the fission chambers.